E-Invoicing Study - Gap Assessment for E-Invoicing Implementation Part 2
Businesses in Malaysia may need to investigate more detail gap assessment after IRBM announced and published E-Invoicing revised guideline version 2.0 and specific guideline version 1.0 on September 29, 2023.
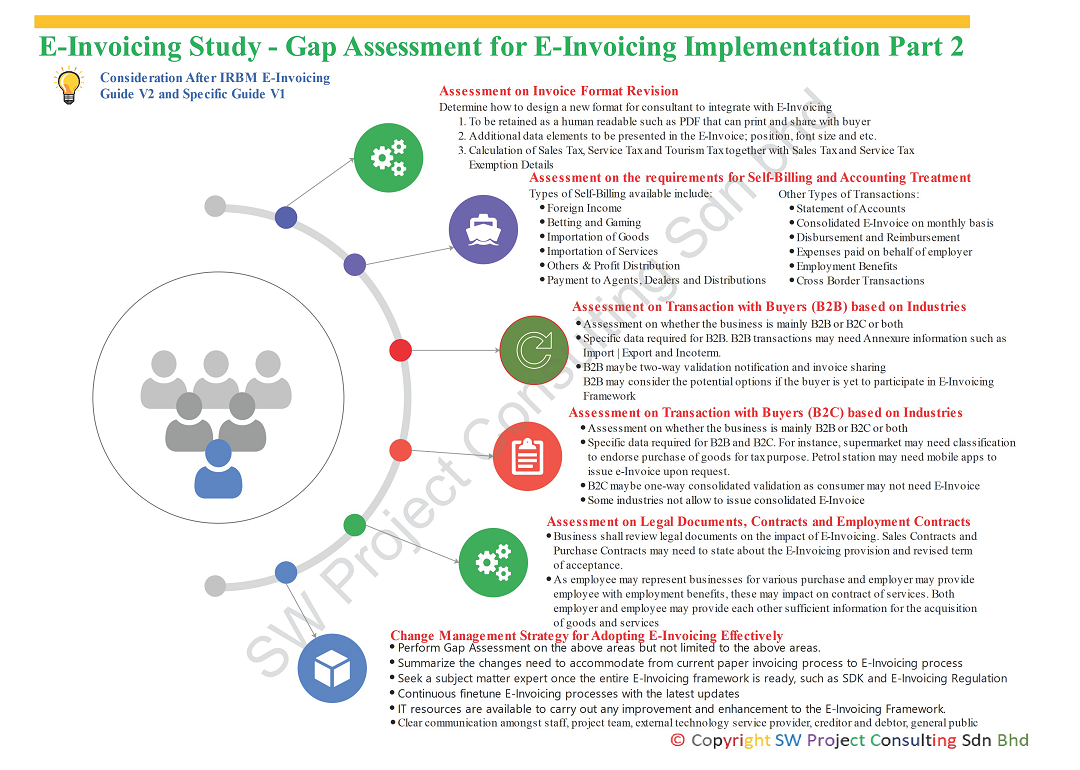
Let's look at additional six areas to address the gap between current process and E-Invoicing process in Part 2:
- Assessment on invoice format revision. The specific guide showed a sample invoice in PDF that consists of more information than the current acceptable invoices with prescribed information. Additional information to display in the new invoice format may include TIN, NRIC, passport, SST ID and other data fields prescribed in the specific guide. The new invoice format must re-design to find places to accommodate new data elements on the invoice. A human readable PDF invoice still requires sharing with recipient or buyer who cannot generate E-Invoice or consumer. Sales Tax and Service Tax and tourism registrants need to ensure that the calculation of tax amount and input exemption details for those qualified with SST exemption.
- Assessment on the requirement of Self-Billing E-Invoice and Accounting Treatment: There are several focus areas that may subject to Self-Billing E-Invoice mechanism. For example, imported service tax will be paid directly to RMCD and at the same time, IRBM needs to issue Self-Billing E-Invoice as part of E-Invoicing mechanism. As such, businesses may need to determine when to trigger the accounting treatment, following the tax point of imported service tax or following the time to raise Self-Billing E-Invoice. Can the ERP or accounting system be issuing E-Invoice without accounting treatment? In addition, If the employee is acting on behalf of the employer to acquire goods and services but does not bring back qualified E-Invoice due to incorrect information stated on E-Invoice, shall the accounting treatment to be triggered as non-tax allowable expenses? Sometimes it is too tedious to ask the supplier to cancel an E-Invoice with a credit note and re-issue a new E-Invoice with all the correct information.
- Assessment of transactions with buyers (B2B) based on industries: This is to assess whether buyers involved are B2B or B2C or both. Additional data elements such as Import | Export | Incoterm needs to be present in the Annexure of E-Invoice. B2B E-Invoicing is two-way verification and sharing of E-Invoice. Businesses may need to consider options for the buyers who are yet to participate in E-Invoicing Framework.
- Assessment of transactions with buyers (B2C) based on industries: This is to assess whether buyers involved are B2B or B2C or both. Businesses may consider specific classification for the goods sold to the consumer as stated in the data catalogue published by IRBM on September 29, 2023. Petrol stations may develop a mobile app for the patron to refill the petrol to issue E-Invoice. Some industries may consolidate all sales to consumer with an E-Invoice while other industries are prohibited to combine into a consolidated E-Invoice. There may not need recipient to receive E-Invoice validation notification.
- Assessment of Legal Documents, Contracts and Employment Contracts: As E-Invoicing will impact the invoicing processes, businesses need to assess whether any updates on legal terms are inside their contracts. Their contracts may need the buyer and the seller to disclose their TIN, SST ID, BRN and Tourism Tax ID whenever it is applicable. Sales Contracts and Purchase Contracts may state E-Invoicing Provisions and revised terms of acceptance. As for the employer that acts on behalf of the employer may need to provide company information such as TIN, BRN, SST ID or Tourism Tax ID to the employer to acquire goods or services. The current structure of the contract of service needs to be reviewed.
- Assessment of a Change Management Strategy for Adopting E-Invoicing Effectively: Once the gap assessment is completed, all findings shall be summarized to support changes from paper-based invoicing process to E-Invoicing process. A subject matter expert shall monitor the entire change process once all information such as SDK and legislation are in order. The subject matter expert shall continue to finetune and improve the implementation of E-Invoice based on the latest amendment and changes. It shall ensure clear communication to all stakeholders such as IT, project team, staff, external technology service provider, creditors, debtors and public. Change management must make sure people, process and technology are in order.