E-Invoicing
This category is to group E-Invoicing articles together
- Details
- Written by: Administrator
- Category: E-Invoicing
- Hits: 1645
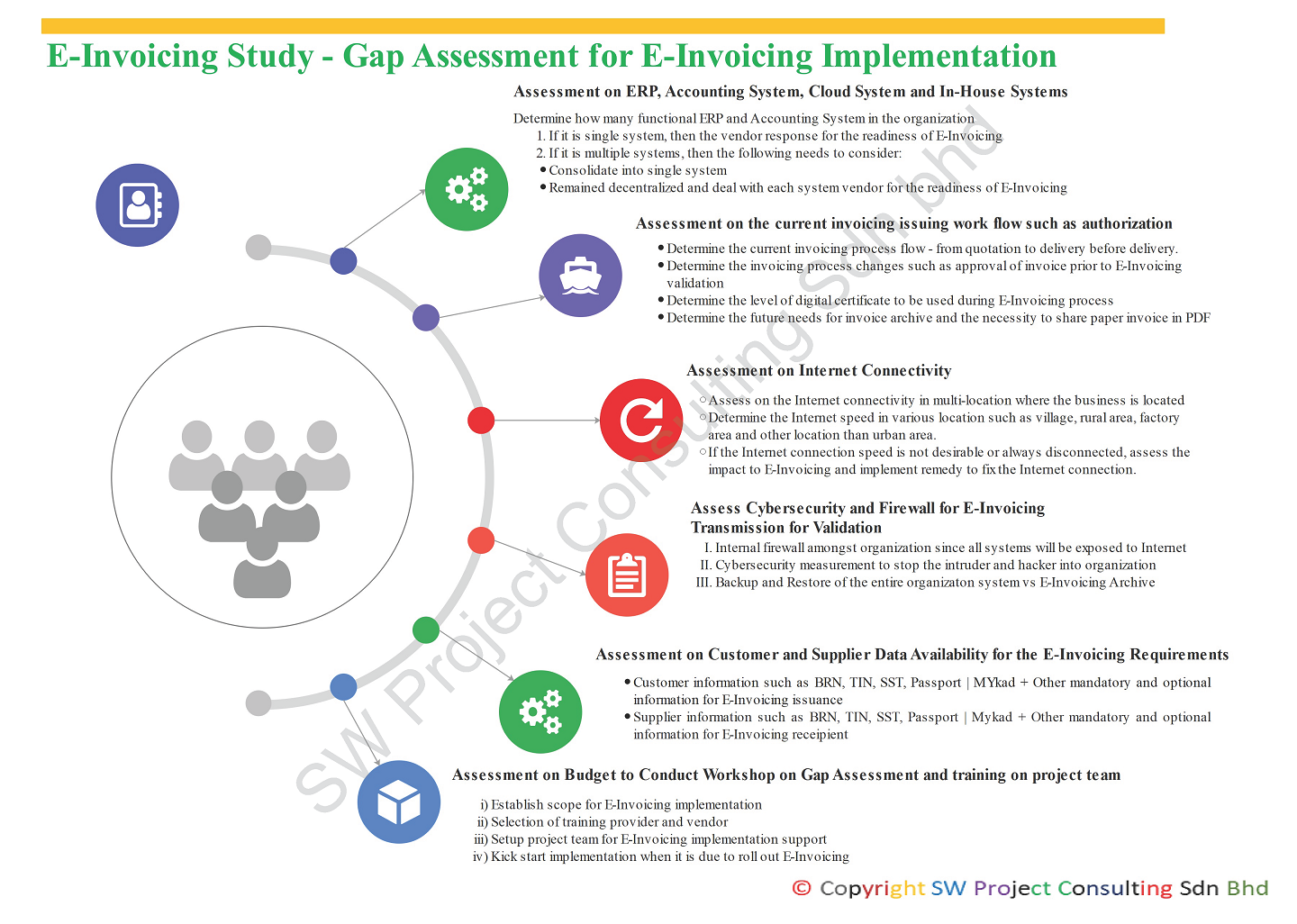
E-Invoicing Study - Gap Assessment for E-Invoicing Implementation
Before E-Invoicing is going to implement in Malaysia in 2024, the organization needs to perform a gap assessment to the current invoicing workflow to determine any procedure changes to accommodate with the E-Invoicing implementation initiative.
Let's look at six areas to address the gap between current process and E-Invoicing process:
- Assessment on ERP, Accounting, Cloud and In-house system: The number of invoicing systems used in the organization. This is to assess the impact of the future direction on whether it shall consolidate into single system for better E-Invoicing operation or remain decentralized to assess the readiness for E-Invoicing integration from different vendors.
- Assessment of the current invoice authorization workflow: This is to assess the current invoice issuing authority so that proper digital signature can be assigned to the right personnel. This is applicable as to the organization using multi-systems and with multi-level authorization to issue and approval invoice. Once the cleared invoice is returned, the organization will consider whether it is still necessary to send PDF invoice to the recipient and archiving options for invoices.
- Assessment of the Internet connection: This is to assess whether invoice generation process needs to be centralized or still decentralized as not all areas will get a strong internet connection. The E-Invoicing validation may post a challenge if the connection with the tax authorization is lagging, slow or disconnected.
- Another assessment in the cybersecurity and firewall: This is to assess the organization firewall can stop cyber-attack from the hackers as to E-Invoices are sent for validation and returned cleared E-invoices to the organization.
- Assessment of customers and vendors data availability: As E-Invoicing will require the master data from the customer such BRN, TIN, SST, MyKad and Passport number. This assessment is to classify data availability of the customers to fit into the organization invoicing generation system. Similarly, the same will apply to the vendors.
- Assessment on budget to conduct workshop and preparation for E-Invoicing implementation: Vendor selection to setup project team and staff training to kick-start E-invoicing implementation.
- Details
- Written by: Administrator
- Category: E-Invoicing
- Hits: 1563
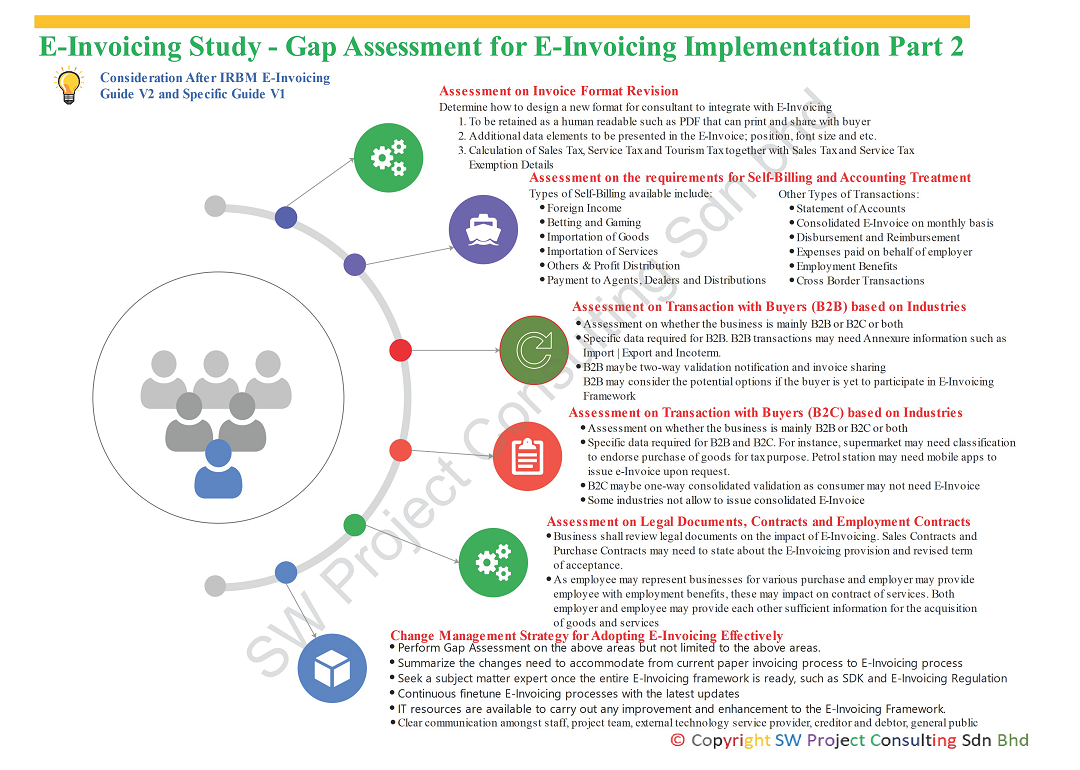
E-Invoicing Study - Gap Assessment for E-Invoicing Implementation Part 2
Businesses in Malaysia may need to investigate more detail gap assessment after IRBM announced and published E-Invoicing revised guideline version 2.0 and specific guideline version 1.0 on September 29, 2023.
Let's look at additional six areas to address the gap between current process and E-Invoicing process in Part 2:
- Assessment on invoice format revision. The specific guide showed a sample invoice in PDF that consists of more information than the current acceptable invoices with prescribed information. Additional information to display in the new invoice format may include TIN, NRIC, passport, SST ID and other data fields prescribed in the specific guide. The new invoice format must re-design to find places to accommodate new data elements on the invoice. A human readable PDF invoice still requires sharing with recipient or buyer who cannot generate E-Invoice or consumer. Sales Tax and Service Tax and tourism registrants need to ensure that the calculation of tax amount and input exemption details for those qualified with SST exemption.
- Assessment on the requirement of Self-Billing E-Invoice and Accounting Treatment: There are several focus areas that may subject to Self-Billing E-Invoice mechanism. For example, imported service tax will be paid directly to RMCD and at the same time, IRBM needs to issue Self-Billing E-Invoice as part of E-Invoicing mechanism. As such, businesses may need to determine when to trigger the accounting treatment, following the tax point of imported service tax or following the time to raise Self-Billing E-Invoice. Can the ERP or accounting system be issuing E-Invoice without accounting treatment? In addition, If the employee is acting on behalf of the employer to acquire goods and services but does not bring back qualified E-Invoice due to incorrect information stated on E-Invoice, shall the accounting treatment to be triggered as non-tax allowable expenses? Sometimes it is too tedious to ask the supplier to cancel an E-Invoice with a credit note and re-issue a new E-Invoice with all the correct information.
- Assessment of transactions with buyers (B2B) based on industries: This is to assess whether buyers involved are B2B or B2C or both. Additional data elements such as Import | Export | Incoterm needs to be present in the Annexure of E-Invoice. B2B E-Invoicing is two-way verification and sharing of E-Invoice. Businesses may need to consider options for the buyers who are yet to participate in E-Invoicing Framework.
- Assessment of transactions with buyers (B2C) based on industries: This is to assess whether buyers involved are B2B or B2C or both. Businesses may consider specific classification for the goods sold to the consumer as stated in the data catalogue published by IRBM on September 29, 2023. Petrol stations may develop a mobile app for the patron to refill the petrol to issue E-Invoice. Some industries may consolidate all sales to consumer with an E-Invoice while other industries are prohibited to combine into a consolidated E-Invoice. There may not need recipient to receive E-Invoice validation notification.
- Assessment of Legal Documents, Contracts and Employment Contracts: As E-Invoicing will impact the invoicing processes, businesses need to assess whether any updates on legal terms are inside their contracts. Their contracts may need the buyer and the seller to disclose their TIN, SST ID, BRN and Tourism Tax ID whenever it is applicable. Sales Contracts and Purchase Contracts may state E-Invoicing Provisions and revised terms of acceptance. As for the employer that acts on behalf of the employer may need to provide company information such as TIN, BRN, SST ID or Tourism Tax ID to the employer to acquire goods or services. The current structure of the contract of service needs to be reviewed.
- Assessment of a Change Management Strategy for Adopting E-Invoicing Effectively: Once the gap assessment is completed, all findings shall be summarized to support changes from paper-based invoicing process to E-Invoicing process. A subject matter expert shall monitor the entire change process once all information such as SDK and legislation are in order. The subject matter expert shall continue to finetune and improve the implementation of E-Invoice based on the latest amendment and changes. It shall ensure clear communication to all stakeholders such as IT, project team, staff, external technology service provider, creditors, debtors and public. Change management must make sure people, process and technology are in order.
- Details
- Written by: Administrator
- Category: E-Invoicing
- Hits: 944
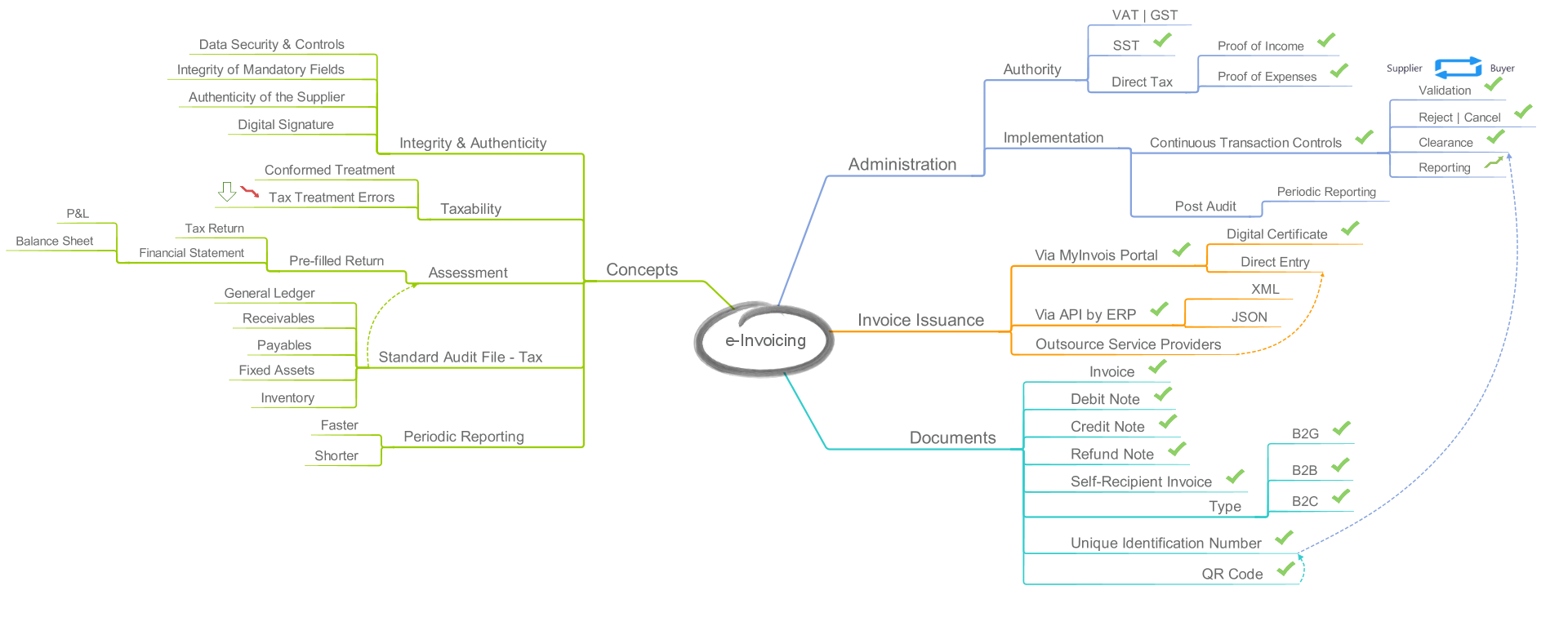
The following slide is an illustration for e-invoicing study - potential legislative amendment in SST Malaysia.
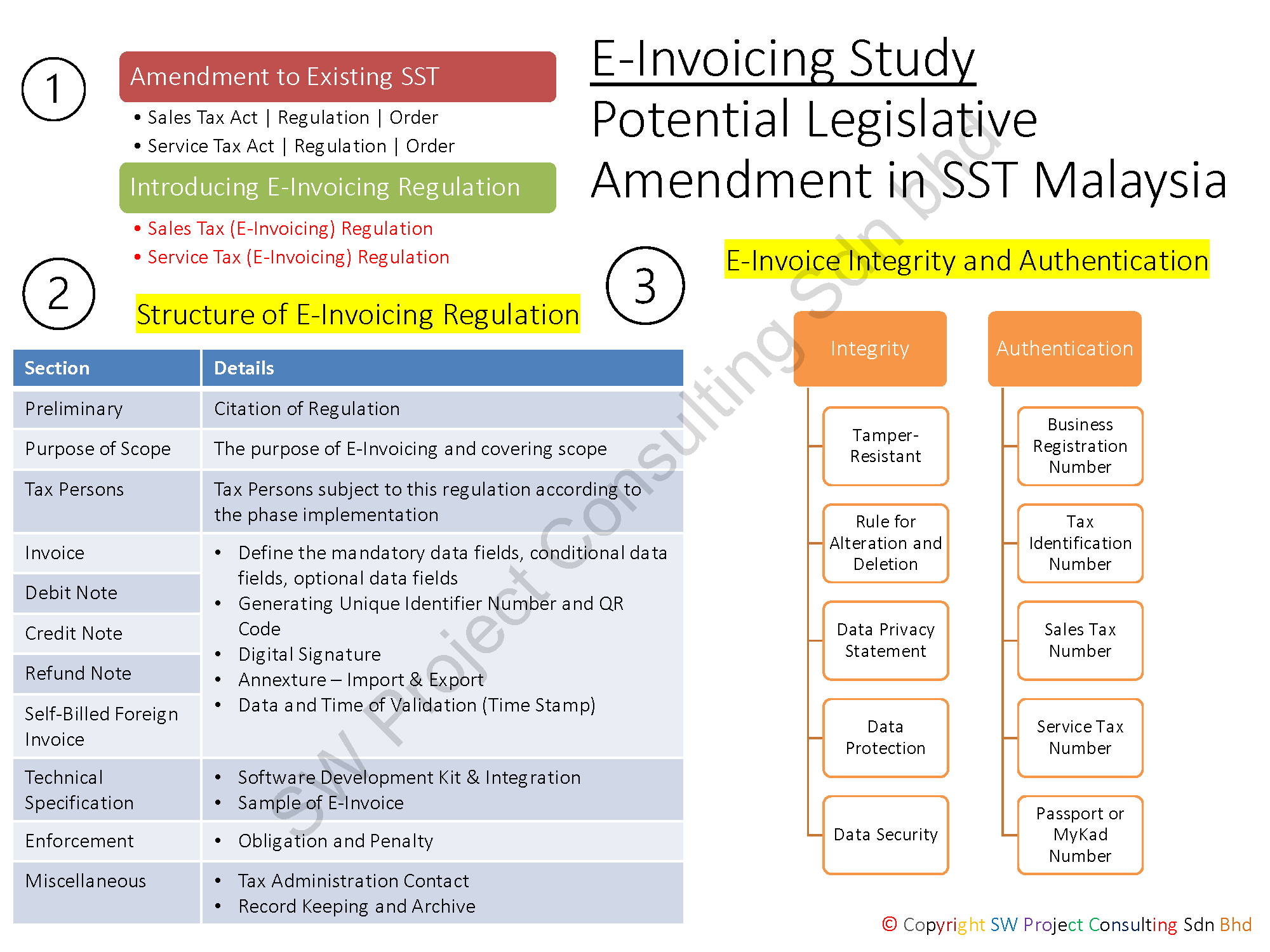 The indirect tax mechanism in Malaysia is a single-stage sales and service tax (SST). It comprises of two independent mechanisms, sales tax, and service tax. respectively.
The indirect tax mechanism in Malaysia is a single-stage sales and service tax (SST). It comprises of two independent mechanisms, sales tax, and service tax. respectively.
To implement electronic invoice or E-Invoice to cover the invoice generation process in SST registrants, the following act needs to be amended and accommodated for whatever impacts to the operation of SST.
- Sales Tax Act 2018
- Service Tax Act 2018
- Sales Tax Regulation (amendment and new legislative document)
- Service Tax Regulation (amendment and new legislative document)
- Sales Tax Order (amendment and new legislative document)
- Service Tax Order (amendment and new legislative document)
If the government introduces new legislative document for E-Invoicing project, the following could be new legislative documents:
- Sales Tax (E-Invoicing) Regulation
- Service Tax (E-Invoicing) Regulation
There are a number of amendments to be made in the E-Invoicing Regulation such as the following:
- Mention about the definition, purpose, and scope of E-Invoicing and how the E-Invoicing is operating in Malaysia
- Tax Persons or SST registrants' involvement in the phase implementation of E-Invoicing project
- Requirements for the business documents such as invoice, credit note, debit note, refund note and self-billed foreign invoice. Amendment details could be some of the details mentioned in the above slide.
- Technical specification - Release of software development kit and integration model. It would be great to provide a sample of XML E-Invoice and whether allow software developer to share PDF/A-3 (with XML embedded) compliant with the buyer.
- Enforcement will highlight on those responsibilities and obligation of the tax administration and SST registrants
- Miscellaneous will highlight on the contact of tax administration division and the method for record keeping and archive mechanism.
E-Invoicing implementation project shall highlight in term of integrity and authentication of E-Invoice as below:
- The integrity of an E-Invoice:
- E-Invoice shall be tamper-resistant for any unlawful changes
- E-Invoice procedure rules on alteration and deletion before validation
- Data privacy statement, Data Protection and Data Security in MyInvois Portal
- The authenticity of an E-Invoice:
- Business Registration Number (BRN)
- Tax Identification Number (TIN)
- Sales Tax Registration Number
- Service Tax Registration Number
- Passport or MyKad Number
Disclaimer:
The above illustration slide is for E-Invoicing study purposes. The views expressed in this article are the author's own views. You must not rely on the information on the slide as an alternative to solicit advice from another appropriately qualified professional.
- Details
- Written by: Administrator
- Category: E-Invoicing
- Hits: 1588
The following visual map is a illustration for 4 corner network diagram for e-invoicing study.
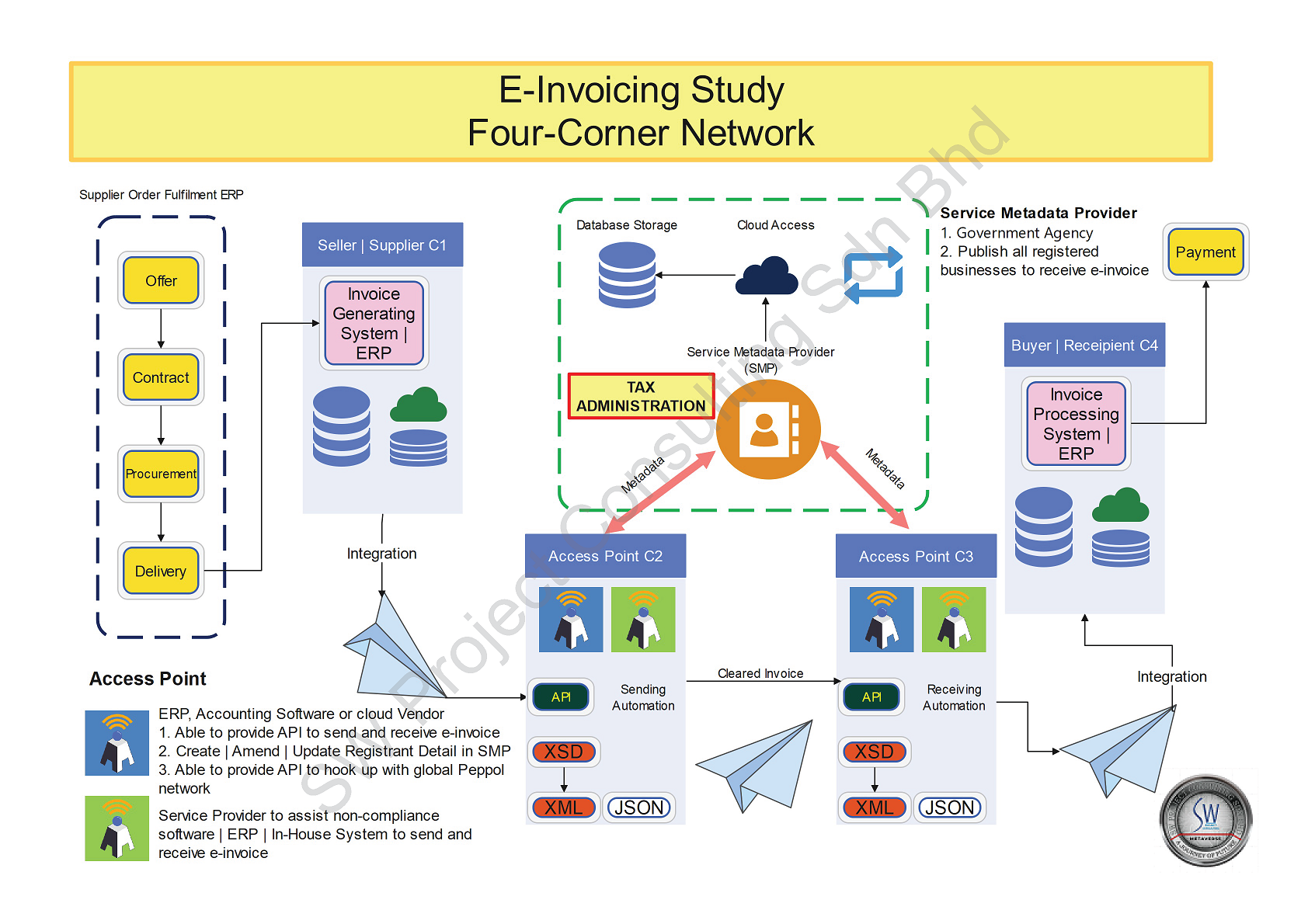
In an E-Invoicing environment, a typical seller will confirm all transaction details via its own order fulfilment ERP so that the invoice can be generated inside invoice generating system ERP as corner 1. Subsequently the access point will be acting as corner 2 to convert the invoice details into an agreed format set by an international body such as PEPPOL or the national tax administration. Access point in this scenario can be an add-in API developed by technical solution provider following business interoperability specification or independent access point service provider who is servicing customer with an in-house, non-compliance accounting or ERP system to send invoice details for validation to service metadata publisher (SMP).
SMP is a government agency such as network information center to monitor and publish all registered businesses who can send and receive e-invoice. After validation from SMP, it will continue to be validated by the tax administration cloud. Once it is validated by the tax administration, it is a cleared invoice. Notification will be sent to corner 2 and corner 3 respectively. A cleared invoice will be sent to corner 3 which represents the access point of the buyer.
Once corner 3 receives a cleared invoice from corner 2, corner 3 will map the cleared invoice into the format of the buyer invoice processing system or accounts payable. Corner 3 can be an add-in API developed by the buyer accounting or ERP system solution provider or independent service provider that is able to map the cleared invoice into in-house | non-compliant accounting or ERP system.
Corner 4 is the invoice processing system, with the details fully verified and validated by the tax administration, it is an approved invoice and therefore it will eliminate all human intervention, data entry and checking for invoice errors. It helps to process payment faster at the end.
- Details
- Written by: Administrator
- Category: E-Invoicing
- Hits: 774
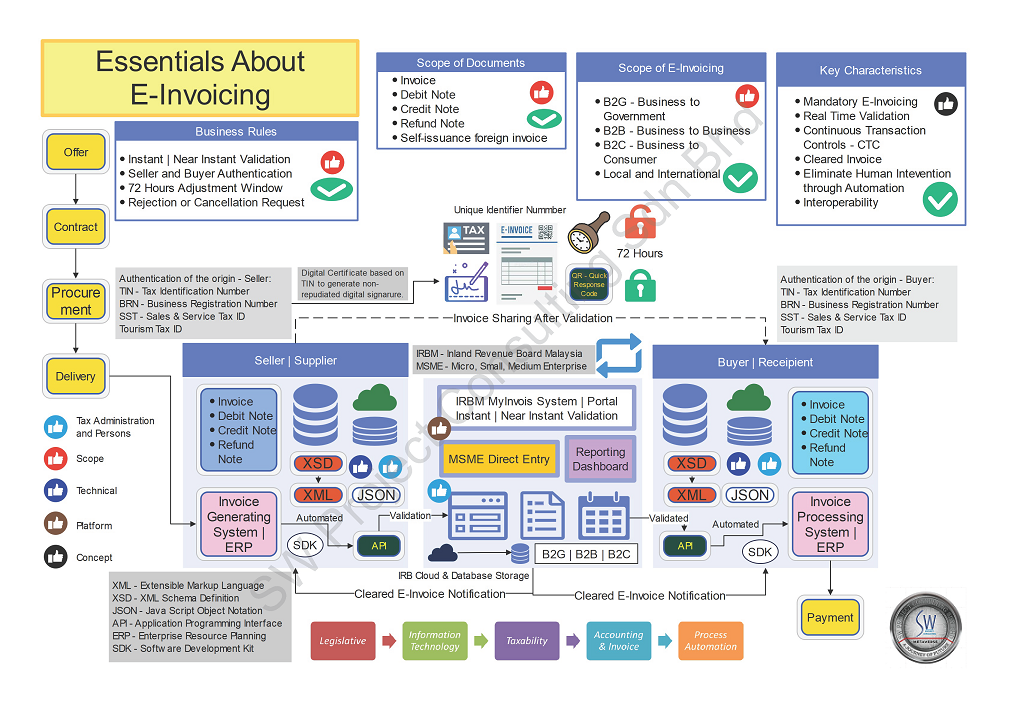
Essentials About E-Invoicing in Summary